As heat pump technology continues to evolve, homeowners and businesses are faced with more choices than ever before. One of the most significant distinctions is between standard (fixed-speed) heat pumps and variable frequency (inverter) heat pumps. But what exactly sets them apart—and why does it matter?
How a Standard Heat Pump Works
Traditional heat pumps operate with a fixed-speed compressor. When heating or cooling is required, the compressor starts at full capacity and runs until the desired temperature is reached. Then it shuts off completely.
This on-off cycling repeats whenever indoor temperatures drift outside the set range.
Key characteristics of a fixed-speed heat pump:
✅ Simpler design
✅ Lower upfront cost
❌ Less precise temperature control
❌ More frequent starts and stops, which can shorten compressor lifespan and increase energy consumption
The Advantages of Variable Frequency (Inverter) Heat Pumps
A variable frequency heat pump, often called an inverter heat pump, uses advanced electronics to continuously adjust compressor speed in response to real-time heating or cooling demand.
Instead of cycling on and off, the compressor ramps up or down to maintain a consistent indoor temperature.
Benefits of inverter technology include:
✅ Higher Efficiency – By avoiding energy-wasting stops and starts, inverter heat pumps can achieve significantly better seasonal performance (higher SCOP and SEER ratings).
✅ Stable Comfort – Temperature stays steady without sudden swings.
✅ Longer Lifespan – Smooth operation reduces mechanical stress and wear.
✅ Quieter Operation – Lower-speed operation is typically much quieter.
In cold climates, inverter heat pumps can also maintain output more effectively in freezing temperatures by adjusting compressor speed to compensate for lower ambient heat.
Energy Savings Over Time
While a standard heat pump can still deliver efficient heating compared to traditional boilers, the difference in annual electricity consumption can be substantial. For example, in regions with long heating seasons, an inverter model may reduce energy use by 20–30% compared to a conventional fixed-speed unit.
Over a lifespan of 15–20 years, these savings can add up to thousands of dollars in reduced operating costs.
Why the Choice Matters
Investing in a variable frequency heat pump is not only about efficiency—it’s also about comfort, durability, and environmental responsibility. As more countries set ambitious climate targets, inverter heat pumps are becoming the preferred solution for residential and commercial heating upgrades.
The Flamingo Commitment to Inverter Technology
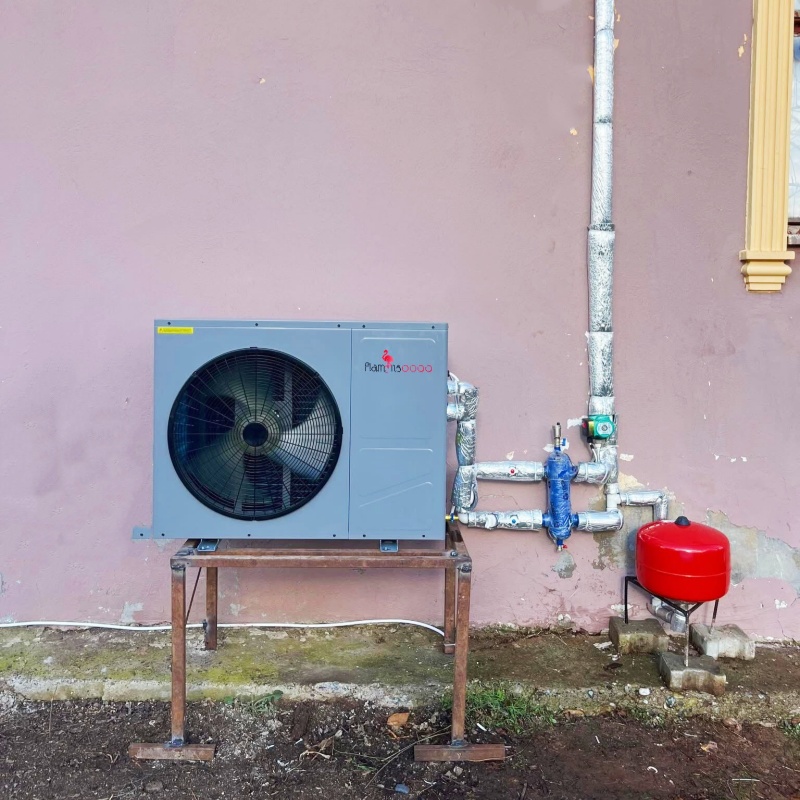
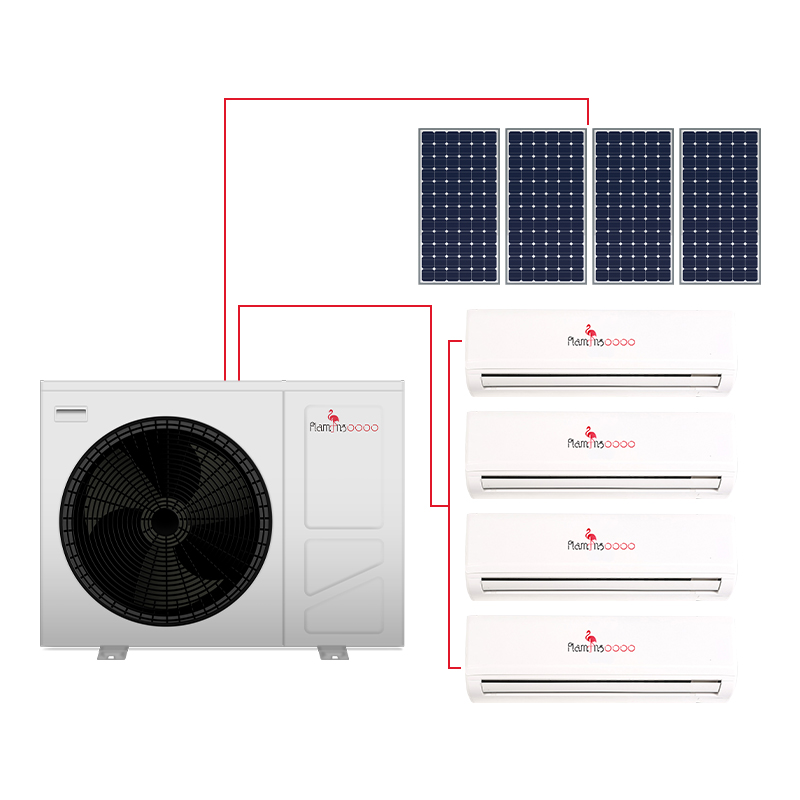
When comparing heat pumps, it’s important to choose a trusted brand with a proven record of innovation and reliability. Flamingo heat pumps are designed to take full advantage of inverter technology, combining advanced compressors with intelligent control systems that adapt precisely to your building’s needs.
From consistently warm floors in winter to quiet, efficient cooling in summer, Flamingo inverter heat pumps deliver performance you can count on—season after season.
Conclusion
The difference between a normal heat pump and a variable frequency heat pump is clear:
✅Fixed-speed models turn fully on or off, leading to less precise control and higher energy consumption.
✅Inverter models continuously adjust output, improving efficiency, comfort, and lifespan.
Whether you are upgrading an existing heating system or planning a new installation, investing in a high-quality variable frequency heat pump is one of the most effective ways to reduce energy bills and create a comfortable, sustainable environment.
Flamingo inverter heat pumps bring together the best of modern technology to help you achieve these goals with confidence.