How Do Heat Pumps Save Energy for Your Home in Cold Winters?
As winter approaches, homeowners face the challenge of keeping their homes warm without breaking the bank. With energy prices fluctuating and environmental concerns on the rise, finding an efficient and sustainable heating solution is more important than ever. Enter heat pumps—an innovative technology that’s transforming how we heat our homes during cold winters. But how exactly do heat pumps save energy, and why are they becoming the go-to choice for homeowners looking to reduce costs and their carbon footprint? In this article, we’ll explore the mechanics of heat pumps, their energy-saving benefits, and why they’re a smart investment for your home.
What Are Heat Pumps and How Do They Work?
Heat pumps are highly efficient heating and cooling systems that transfer heat from one place to another. Unlike traditional heaters that generate heat by burning fuel or using electric resistance, heat pumps move heat from the outside air, ground, or water into your home. This process makes them incredibly energy-efficient, even in freezing temperatures.
The Science Behind Heat Pumps
At the core of a heat pump’s operation is a refrigeration cycle that involves four main components: the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it works:
Evaporator: The heat pump extracts heat from an external source, such as the outside air or the ground, even when temperatures are low. A refrigerant absorbs this heat and turns into a gas.
Compressor: The gas is compressed, which increases its temperature significantly.
Condenser: The hot gas releases its heat into your home’s heating system, warming the air or water that circulates through your house.
Expansion Valve: The refrigerant cools down and returns to a liquid state, ready to start the cycle again.
This process allows heat pumps to provide warmth using significantly less energy than traditional heating systems like furnaces or electric heaters.
Types of Heat Pumps
There are several types of heat pumps, each suited to different climates and home setups:
Air-Source Heat Pumps: These extract heat from the outside air and are the most common type. They work well in moderate to cold climates and are relatively easy to install.
Ground-Source (Geothermal) Heat Pumps: These use the stable temperature of the ground or water sources to transfer heat. They’re highly efficient but require more extensive installation.
Water-Source Heat Pumps: These draw heat from a nearby water source, such as a lake or well, and are less common but highly effective in specific settings.
Each type has its advantages, but air-source heat pumps are particularly popular for their versatility and affordability, making them ideal for most homes facing cold winters.

Why Heat Pumps Excel in Cold Weather
One common misconception is that heat pumps are ineffective in cold climates. While early models struggled in sub-zero temperatures, modern heat pumps are designed to perform efficiently even in harsh winters. Advances in technology, such as variable-speed compressors and low-temperature refrigerants, allow heat pumps to extract heat from the air at temperatures as low as -15°F (-26°C) or lower.
Energy Efficiency: The Key to Savings
The primary reason heat pumps save energy is their high coefficient of performance (COP). The COP measures how much heat a system produces per unit of energy consumed. For example, a heat pump with a COP of 3 delivers three units of heat for every unit of electricity used. In contrast, traditional electric heaters have a COP of 1, meaning they use one unit of electricity to produce one unit of heat. This efficiency translates directly into lower energy bills.
In cold winters, when heating demands are high, heat pumps maintain their efficiency by leveraging ambient heat sources. Even when it’s freezing outside, there’s still thermal energy in the air or ground that a heat pump can tap into. This makes them far more cost-effective than gas furnaces or electric resistance heaters, which lose efficiency as temperatures drop.
Backup Heating for Extreme Cold
For regions with prolonged sub-zero temperatures, many heat pumps come with a backup heating system, such as electric resistance coils, to supplement heating on the coldest days. While this backup system is less efficient, it’s rarely needed, ensuring that your overall energy consumption remains low.
Financial Benefits of Heat Pumps in Winter
Switching to a heat pump can lead to significant cost savings, especially during the winter months when heating bills typically spike. Here’s how heat pumps help you save money:
Lower Energy Bills
Because heat pumps use electricity to move heat rather than generate it, they consume less energy overall. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, homeowners can save up to 50% on heating costs by switching from traditional systems to a heat pump. For a typical household spending $1,000 annually on heating, this could mean savings of $500 or more each winter.
Reduced Maintenance Costs
Heat pumps are generally low-maintenance compared to gas furnaces or boilers. They don’t require regular fuel deliveries or combustion-related maintenance, such as chimney cleaning. With proper care, a heat pump can last 15–20 years, reducing long-term replacement and repair costs.
Incentives and Rebates
Many governments and utility companies offer incentives to encourage the adoption of energy-efficient technologies like heat pumps. In the United States, for example, the Inflation Reduction Act provides tax credits and rebates for installing high-efficiency heat pumps. Similar programs exist in Canada, the European Union, and other regions, making the upfront cost more affordable.
Environmental Benefits of Heat Pumps
In addition to saving money, heat pumps are an environmentally friendly choice. As the world moves toward decarbonization, reducing reliance on fossil fuels is critical. Heat pumps contribute to this goal in several ways:
Lower Carbon Emissions
Since heat pumps run on electricity and don’t burn fossil fuels, they produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions than gas or oil furnaces. As the electrical grid becomes increasingly powered by renewable sources like wind and solar, the carbon footprint of heat pumps will shrink even further.
Reduced Reliance on Fossil Fuels
By using ambient heat from the air or ground, heat pumps eliminate the need for natural gas, propane, or oil. This not only reduces emissions but also helps homeowners avoid the price volatility associated with fossil fuel markets.
Support for Renewable Energy Integration
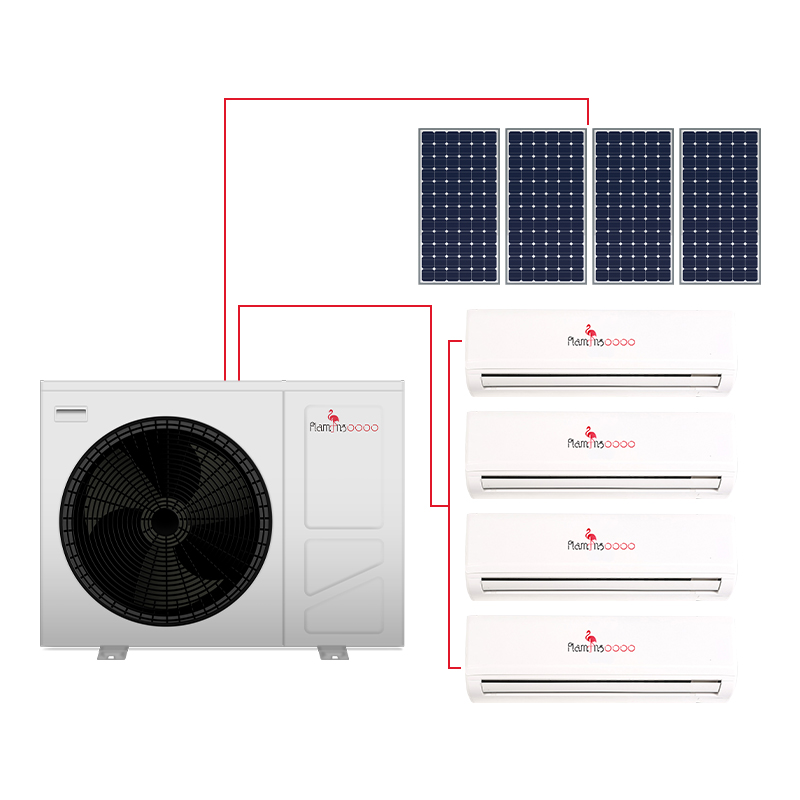
Heat pumps pair well with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels. Homeowners with solar installations can power their heat pumps with clean energy, further reducing their environmental impact and energy costs.
Choosing the Right Heat Pump for Your Home
Selecting the right heat pump depends on several factors, including your climate, home size, and budget. Here are some key considerations:
Climate Compatibility
For cold climates, look for a heat pump with a high Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF), which measures its efficiency in heating mode. Models with variable-speed compressors and low-temperature capabilities are ideal for harsh winters.
Sizing and Installation
A properly sized heat pump is critical for maximizing efficiency. An oversized unit will cycle on and off too frequently, wasting energy, while an undersized unit will struggle to keep your home warm. Work with a qualified HVAC contractor to perform a load calculation and ensure proper installation.
Integration with Existing Systems
Heat pumps can often be integrated with existing ductwork or paired with a backup heating system. Ductless mini-split heat pumps are a great option for homes without ducts, offering flexible installation and zoned heating.
Overcoming Common Concerns About Heat Pumps
Despite their benefits, some homeowners hesitate to switch to heat pumps due to concerns about cost, performance, or installation. Let’s address these concerns:
Upfront Costs
While heat pumps have a higher initial cost than some traditional systems, the long-term savings and available incentives often offset this expense. Financing options and rebates can further reduce the financial burden.
Performance in Extreme Cold
As mentioned earlier, modern heat pumps are designed for cold climates. Choosing a model with advanced features, such as inverter technology, ensures reliable performance even in sub-zero temperatures.
Installation Challenges
While ground-source heat pumps require significant upfront installation, air-source and ductless systems are relatively straightforward to install. Working with an experienced contractor minimizes disruptions and ensures optimal performance.
Tips for Maximizing Heat Pump Efficiency
To get the most out of your heat pump in winter, follow these tips:
Regular Maintenance: Schedule annual maintenance to keep your heat pump running efficiently. Clean or replace filters regularly to ensure proper airflow.
Smart Thermostats: Use a programmable or smart thermostat to optimize heating schedules and reduce energy waste.
Insulate Your Home: Proper insulation and weatherization prevent heat loss, allowing your heat pump to work more efficiently.
Zoned Heating: If using a ductless system, take advantage of zoned heating to warm only the rooms you’re using.
Monitor Performance: Keep an eye on your heat pump’s performance and address any issues promptly to avoid efficiency losses.
The Future of Heating: Why Heat Pumps Are Here to Stay
As energy efficiency and sustainability become top priorities, heat pumps are poised to dominate the heating market. Governments worldwide are promoting their adoption through incentives and regulations, while manufacturers continue to innovate, making heat pumps more efficient and affordable.
Policy Support
In the European Union, the REPowerEU plan aims to install 10 million heat pumps by 2027 to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Similarly, the U.S. and Canada are expanding tax credits and rebates to encourage homeowners to switch to heat pumps.
Technological Advancements
Ongoing research is improving heat pump performance in extreme climates, reducing costs, and integrating smart technology for better control. Innovations like hybrid heat pumps, which combine heat pumps with other heating sources, offer even more flexibility.
Growing Consumer Awareness
As more homeowners experience the benefits of heat pumps, word-of-mouth and positive reviews are driving demand. Online searches for “heat pumps for winter heating” have surged, reflecting growing interest in this technology.
Conclusion: A Smart Choice for Winter Savings
Heat pumps are revolutionizing home heating by offering an energy-efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional systems. By transferring heat rather than generating it, they save energy, reduce bills, and lower carbon emissions, making them an ideal choice for cold winters. With government incentives, technological advancements, and growing consumer adoption, now is the perfect time to consider a heat pump for your home.
Ready to make the switch? Contact a local HVAC professional to explore your options and start saving energy this winter. For more information on heat pumps and other energy-saving solutions, visit our website and join the thousands of homeowners embracing a greener future.